Have you ever created something digital, only to find it copied without permission? Copyright infringement costs creators billions yearly. This is where blockchain technology steps in as a practical solution for protecting ownership rights in ways traditional systems simply cannot match.
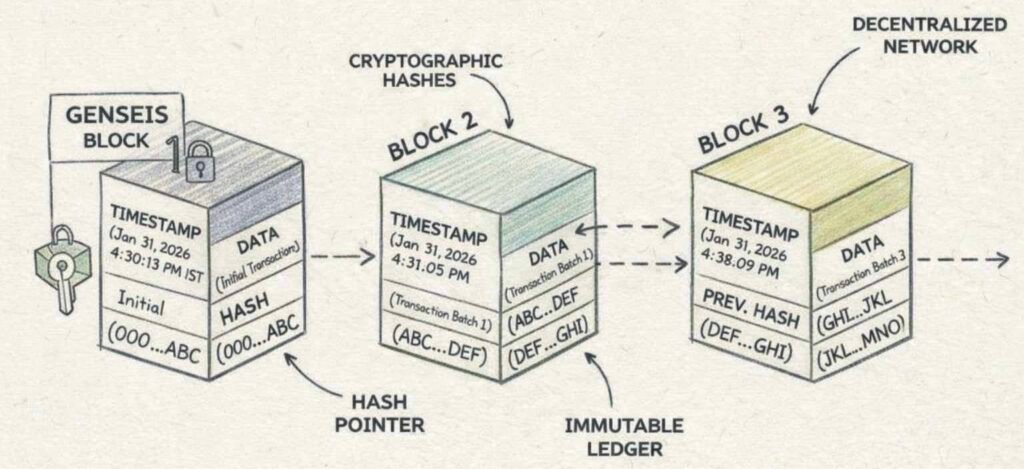
At its core, blockchain acts as a decentralized digital ledger that records transactions across multiple computers, making data extremely resistant to tampering. For intellectual property management, this means creators can timestamp their work on an unchangeable chain, establishing verifiable proof of existence from the moment of creation. Unlike traditional copyright registration, which takes days and involves middlemen, blockchain offers near-instant protection accessible anywhere in the world.
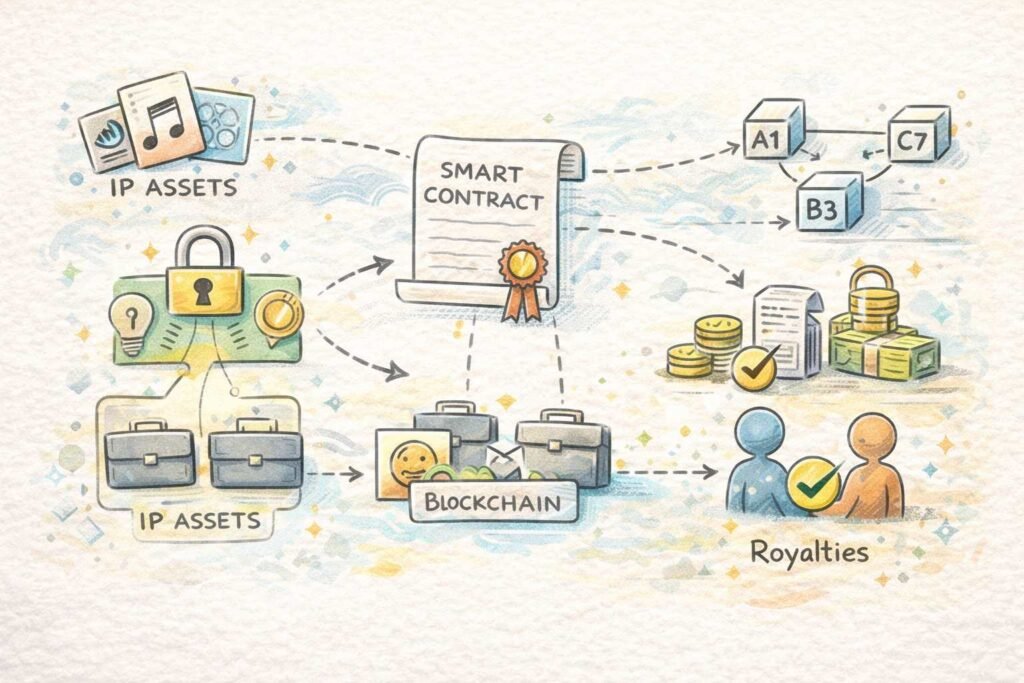
Beyond simple timestamping, blockchain enables smart licenses—automated contracts that handle royalty calculations and payments without needing trusted third parties. This changes how creators earn from their work, removing the blind trust traditionally required between licensors and licensees. The technology democratizes IP protection, making it affordable for individual creators who couldn’t previously afford expensive legal processes.
Two Ways to Read This Series
- New here? Begin with blockchain basics to understand how immutable records work through distributed consensus.
- Continuing the journey? You already know the foundation. Now let’s see how this same mechanism enables transformative applications like intellectual property protection.
How Blockchain Protects Intellectual Property
Traditional IP protection has real problems: centralized databases get hacked, ownership records stay murky, and audits cost a fortune. Blockchain fixes these through three main features.
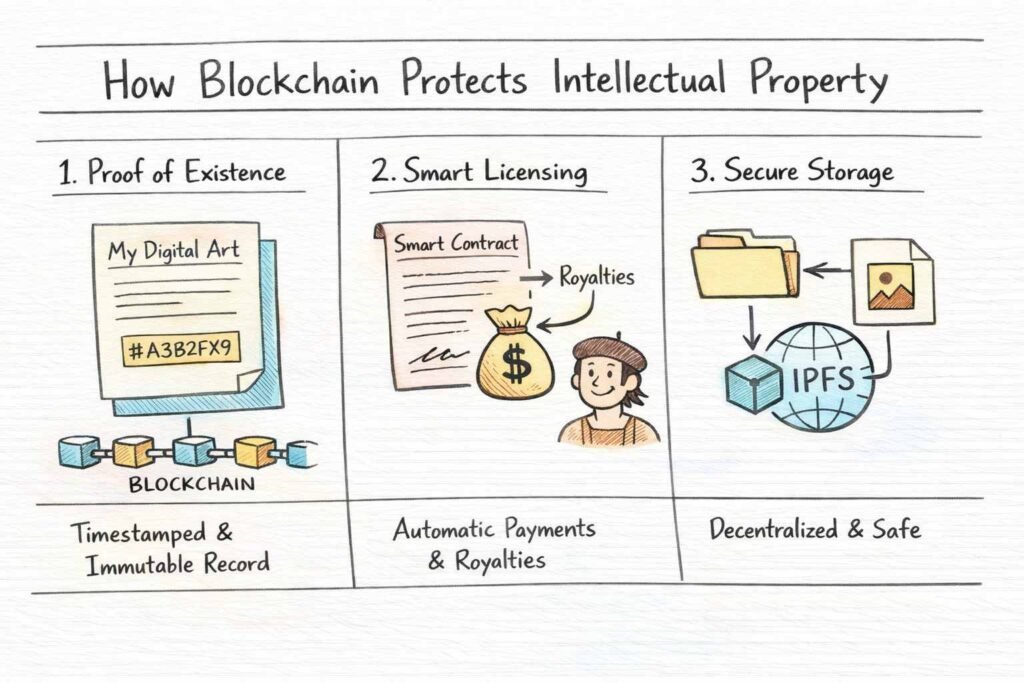
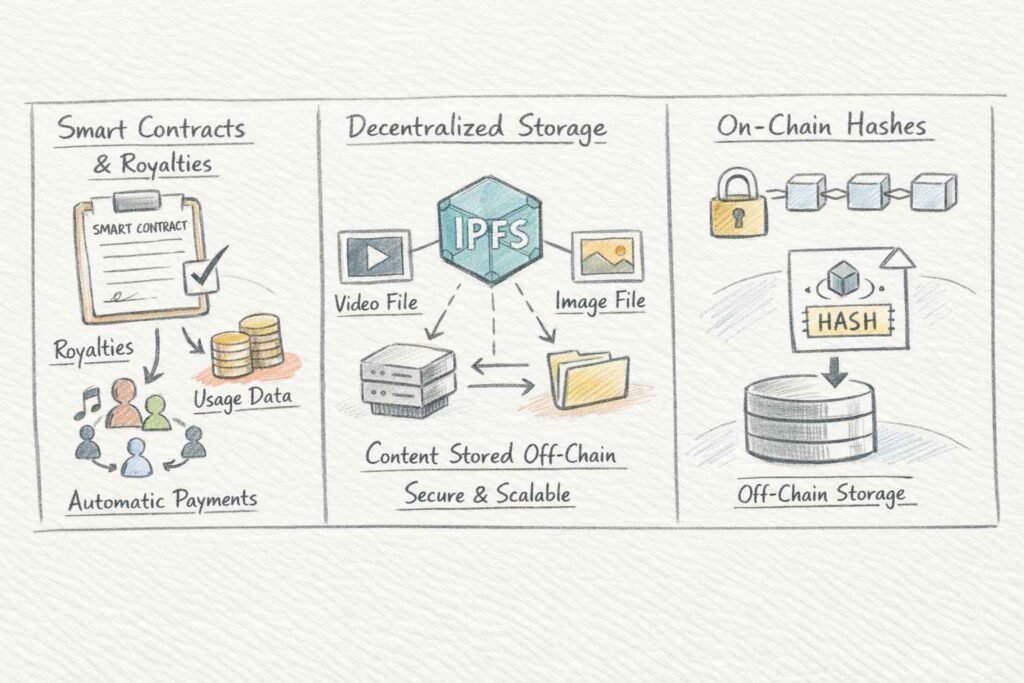
1. Cryptographic Proof of Existence
When someone uploads content to a system like SmartRegistry-IP, the platform creates a unique hash—think of it as a digital fingerprint—that gets permanently recorded on the chain. Even if someone copies the work later, the creator holds timestamped proof that predates the infringement. Courts increasingly accept blockchain records as legal evidence of first publication.
2. Automated Licensing with Smart Contracts
These self-executing agreements contain royalty logic that automatically calculates and distributes payments based on actual usage. Everyone accesses the same transparent information, so expensive audits become unnecessary. Licensees cannot underreport usage, and creators see exactly how their work performs.
3. Decentralized Storage (IPFS Integration)
Decentralized storage solutions like IPFS (InterPlanetary File System) store actual content off-chain while keeping cryptographic hashes on-chain. This hybrid approach achieves both security and scalability—large media files stay accessible while ownership proofs remain tamper-proof.
Blockchain in Healthcare: Protecting Patient Information
Healthcare faces unique data security challenges. Medical records contain sensitive personal information, yet must remain accessible to authorized providers across different institutions. Traditional centralized systems create single points of failure—one breach can expose millions of records. Blockchain in healthcare offers a different approach, prioritizing both security and controlled access.
Modern blockchain healthcare systems combine multiple security layers. When patient data enters the system, strong encryption algorithms protect it. The encrypted data is spread across decentralized storage networks, while only cryptographic hashes remain on the blockchain. Even if attackers breach one storage node, they cannot reconstruct complete patient records without the encryption keys scattered across the network.
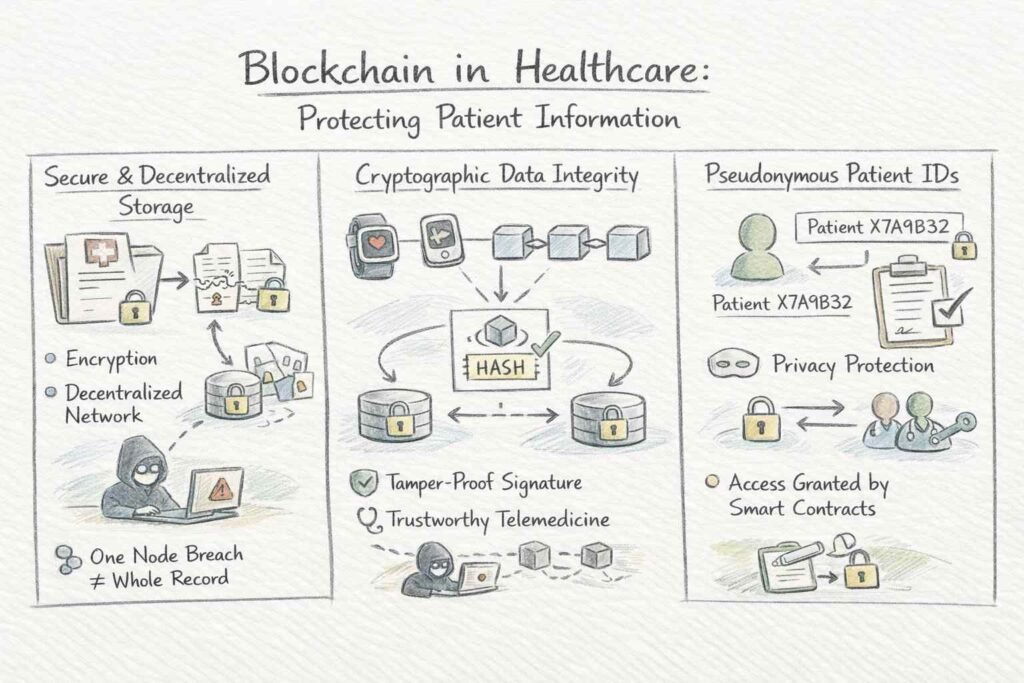
Access control represents another breakthrough. Smart contracts enforce detailed permission policies—patients grant temporary access to specific providers for limited time periods. Every access attempt is recorded permanently, creating audit trails showing exactly who viewed what and when. The system can even use biometric authentication to allow compromised credentials to be replaced—a capability often impossible with traditional passwords.
For IoT healthcare devices monitoring patients continuously, blockchain ensures data integrity from source to storage. Each reading receives a cryptographic signature, preventing unauthorized changes between the device and the medical record. This proves invaluable for telemedicine, where providers must trust remote monitoring data for treatment decisions.
Blockchain in Cryptocurrency Trading
While IP and healthcare show blockchain’s security applications, cryptocurrency trading reveals its natural capabilities for value transfer. When traders execute transactions, blockchain performs critical functions that traditional financial systems cannot match.
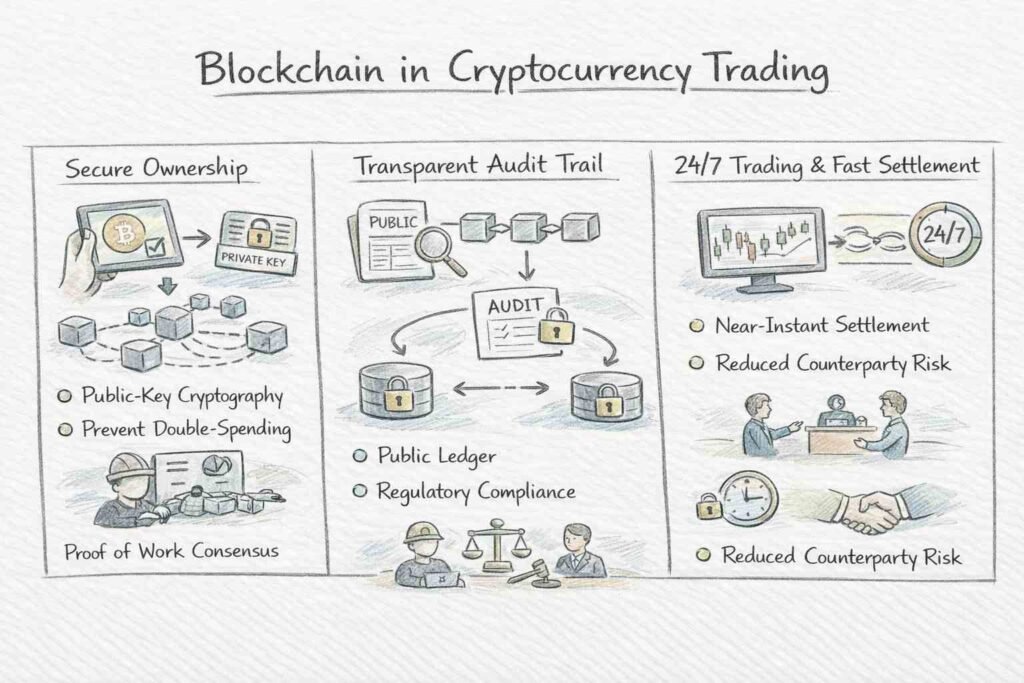
The technology verifies ownership through public-key cryptography. Each user holds a private key—essentially a secure password—proving control over assets without revealing their identity. Transactions are broadcast to the network, where consensus mechanisms such as Proof of Work validate them before permanent recording. This prevents double-spending, where someone might try to transfer the same asset twice.
Blockchain creates transparent audit trails of all trading activity. Every transaction, from an asset’s creation through every subsequent transfer, remains visible on the public ledger. This transparency aids regulatory compliance and dispute resolution. Unlike traditional finance, where records sit in isolated institutional databases, blockchain’s distributed nature means no single party can alter the transaction history.
The technology enables 24/7 trading with near-instant settlement. Traditional securities trading involves clearing houses and settlement periods lasting days. Blockchain transactions settle in minutes, reducing counterparty risk and freeing up capital faster.
How Blockchain Protects Privacy
Many misunderstand blockchain’s privacy model. Public blockchains don’t expose everything to everyone—they use sophisticated privacy mechanisms to protect identities while maintaining transaction integrity.
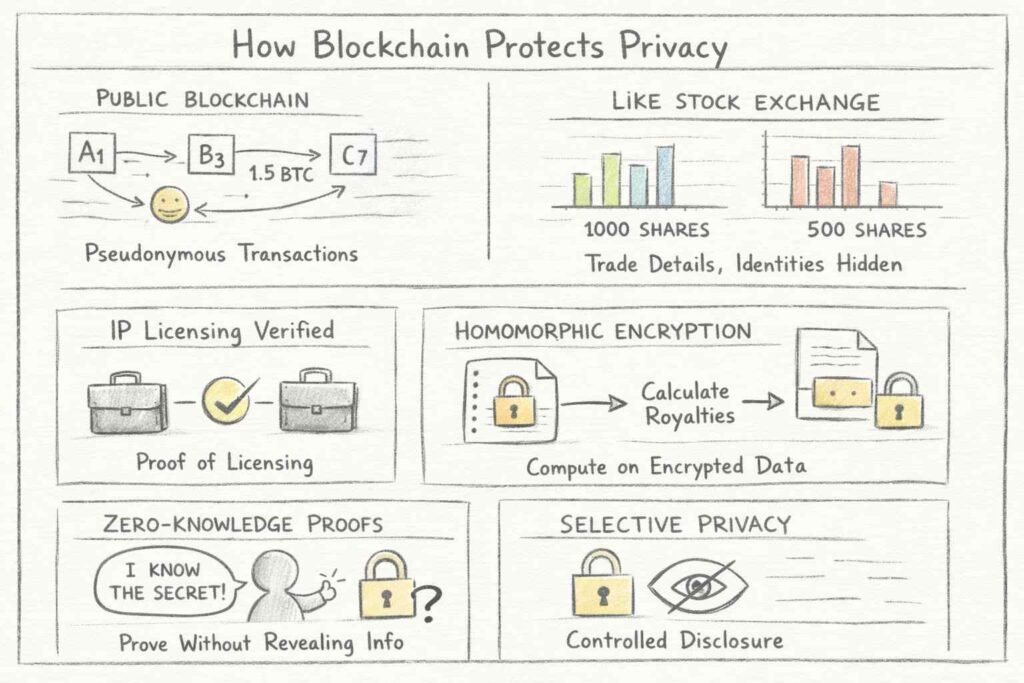
Bitcoin’s original design showed this: The public sees transactions between pseudonymous addresses without identifying the parties involved. This resembles stock exchange data where trade sizes appear publicly, but trader identities stay confidential unless disclosed. For IP transactions, competitors can verify that licensing occurred without accessing sensitive commercial terms.
Advanced privacy techniques enhance confidentiality further. Homomorphic encryption allows computations on encrypted data—royalties are calculated accurately without decrypting the underlying sales figures. Zero-knowledge proofs let one party prove they possess certain information without revealing the information itself. These tools transform blockchain from completely transparent to selectively transparent.
For healthcare, pseudonymity proves essential. Patient records link to cryptographic identifiers rather than names, preventing casual observers from connecting medical histories to individuals. Yet authorized providers can access complete records when patients grant permission through smart contracts. The system creates “walled gardens” within the blockchain—data stays accessible only to parties holding the appropriate keys.
Conclusion
Blockchain transforms data security from reactive breach prevention to proactive verified ownership. For intellectual property, it gives creators immediate, verifiable proof of ownership without expensive intermediaries. For healthcare, it gives patients control over sensitive information while ensuring providers can access accurate records when needed.
The common thread is the replacement of institutional trust with cryptographic verification. Rather than trusting licensees to report royalties accurately or hospitals to secure databases, blockchain makes compliance mathematically inevitable. Smart licenses compute payments automatically. Encrypted records stay accessible only to key holders. Transaction histories persist permanently for auditing.
The foundation exists. The question is how creatively we apply it.
Have you encountered situations where proving digital ownership or securing sensitive data could transform your work? Share your thoughts below.